What is Vertical Analysis? Process & Examples

IT and software costs have increased on a dollar basis, which could initially cause some concern for FP&A executives looking to cut costs. However, when reviewed against the overall revenue of the business, this line item has actually gone down slightly. Take, for example, applying vertical analysis to compare employee salaries with revenue. Over three years, you might notice salaries increasing from 31% to 42% of revenue. Since vertical analysis presents results as percentages, it’s clear that salaries are rising in relation to revenue changes.
Free Cash Flow and Other Valuation Statements
This approach allows for meaningful comparisons of line items over time or across companies, highlighting changes in the composition and structure of financial statements. This method expresses each line item on a financial statement as a percentage of a key benchmark, typically total revenue (in the case of the income statement) or total assets (for the balance sheet). It allows stakeholders, including investors, analysts, and management, to gain valuable insights into a company’s ledger account financial structure and performance.
Vertical Analysis – Formula
- This method allows stakeholders to quickly identify trends and anomalies that might not be apparent through raw numbers alone.
- These results can then be compared for historic performance analysis of the stock or against the industry benchmarks.
- Vertical analysis is a useful tool for financial statement analysis and helps businesses gain insight into their financial position and performance.
- To perform such analysis, one needs to create a common size financial statement (for example, a common size income statement).
- By doing this, we’ll build a new income statement that shows each account as a percentage of the sales for that year.
- We’re firm believers in the Golden Rule, which is why editorial opinions are ours alone and have not been previously reviewed, approved, or endorsed by included advertisers.
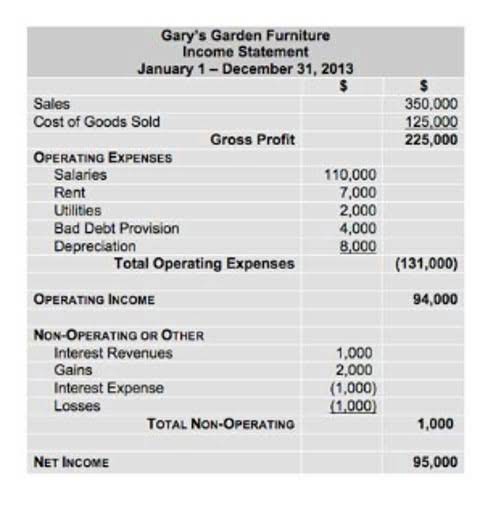
ABC Company’s income statement and vertical analysis demonstrate the value of using common-sized financial statements to better understand the composition of a financial statement. It also shows how a vertical analysis can be very effective in understanding key trends over time. By standardizing financial data into percentages, vertical analysis enables comparisons between companies of different sizes within the same industry. This is particularly useful for investors and analysts who need to benchmark a company’s performance against its peers. For instance, if one company’s administrative expenses are 10% of sales while an industry average is 5%, this https://www.bookstime.com/ discrepancy can prompt further investigation into the company’s cost management practices. Horizontal analysis, also known as trend analysis, compares historical data on a financial statement over different accounting periods.

The Income Statement
Therefore, line items on an income statement can be listed as a percentage of the business’s gross sales. While line items on a company’s balance sheet can be listed as a percentage of total assets or liabilities. When you apply vertical analysis to the balance sheet, you can understand the relative composition of assets, liabilities, and equity.
Importance of Vertical Analysis in Financial Analysis
In this type of analysis, each line item is represented as a percentage of another item. Usually, a baseline item is selected and all other items are reported in percentage terms of that item. You simply receive a concise view of your line items without performing complex calculations. Using tools such as Power BI to chart your results, you can visualize your performance and make informed decisions for a successful plan. After all, as a company scales, you would expect both costs and revenue to go up.

Integrating vertical analysis with horizontal analysis can provide a more comprehensive understanding of a company’s financial performance. While vertical analysis focuses on the proportional relationships within a single period, horizontal analysis examines changes over multiple periods. By combining these two methods, stakeholders can gain insights into both the structure and the trajectory of financial metrics.
- Vertical analysis looks at numbers in financial statements in the same period and calculates each line item as a percentage of the base figure in that section.
- Financial statements are maintained by companies daily and used internally for business management.
- To deepen your understanding of vertical analysis, let’s explore some practical examples that demonstrate its application in analyzing financial statements.
- This approach allows for a clear visualization of how each expense category impacts overall revenue, making it easier to spot inefficiencies or areas for improvement.
- Creating visually appealing charts such as bar graphs or data tables will make it easier to understand.
- When we carry out vertical analysis on the income statement, it shows the top-line sales figure as 100% and every other item is shown as percentage of the total sales for that year.

Finally, the net income margin is 40%, indicating that 40% of the company’s net sales translates into net income. Furthermore, by accessing up-to-date data, you can make informed decisions based on a comprehensive understanding of your financial performance. The ability to create charts, graphs, and visual vertical analysis formula representations of financial data simplifies the planning process and enhances decision-making capabilities. This information will provide a better understanding of which areas of your company are generating high and low revenue.
By Industry
First, we can see that the company’s marketing expenses increased not just in dollar terms, but also as a percentage of sales. This implies that the new money invested in marketing was not as effective in driving sales growth as in prior years. Want to learn how Cube can help you conduct vertical analysis effectively (and in less time)?
There are no comments
Add yours